Solid-state batteries offer higher energy density and safety than conventional lithium-ion batteries. They replace the liquid electrolytes with solid counterparts.
Exploring the realm of battery technology reveals a significant evolution from lithium-ion to solid-state batteries. As the quest for more efficient, powerful, and safer energy storage continues, the transition to solid-state technology marks a promising advancement. Solid-state batteries stand out with their robust energy density, allowing longer-lasting power without frequent recharges.
This is a game-changer for industries like electric vehicles and consumer electronics, where battery life and stability are paramount. The absence of flammable liquid electrolytes in solid-state batteries also means improved safety, reducing the risk of fires and explosions. Despite these advantages, lithium-ion batteries dominate the market due to their established manufacturing processes and lower cost. However, the potential of solid-state technology is undeniable, as it promises to revolutionize the way we store and use energy.
Solid State Battery Vs Lithium Ion
Solid-state batteries and lithium-ion batteries are two leading types of rechargeable batteries, each with unique advantages and drawbacks. Solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid or gel found in lithium-ion batteries. This key difference offers several advantages such as higher energy density, longer life cycles, and improved safety due to reduced risk of leaks and fires. However, they are currently more expensive and challenging to manufacture at scale. Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, are well-established in the market, offering high energy density, reasonable cost, and widespread availability, making them the current standard for most portable electronic devices and electric vehicles.
While solid-state batteries hold promise for the next wave of energy storage solutions, ongoing research and development are crucial for addressing their production and cost challenges.

Introduction To Battery Evolution
The journey of battery technology is a tale of innovation and discovery. Over the years, battery design has evolved significantly, powering our gadgets and vehicles with greater efficiency and reliability. Let’s explore this exciting evolution from its humble beginnings to the cutting-edge advancements of today.
From Lead-acid To Lithium Ion
Batteries began with the simple lead-acid type, first invented in the mid-1800s. These batteries were heavy and had low energy density. By the late 20th century, lithium-ion batteries emerged. They offered a leap in performance, with higher energy density and longer life spans.
- Lead-acid: Heavy, low energy density
- Nickel-cadmium: Better performance, but toxic
- Nickel-metal hydride: Less toxic, used in early hybrid cars
- Lithium-ion: High energy density, rechargeable, widely used today
Rise Of Solid State Technology
The latest chapter in battery evolution is the rise of solid-state technology. These batteries promise even higher energy density and safety compared to lithium ions. They use solid electrolytes instead of liquid, removing the risk of leaks and reducing the chance of fire.
- Improved safety: Solid electrolytes prevent leaks
- Increased energy density: More power contained in a smaller unit
- Longer lifespan: Degradation over time is slower
Solid-state batteries are still in development but are set to revolutionize how we store and use energy.
Credit: article.murata.com
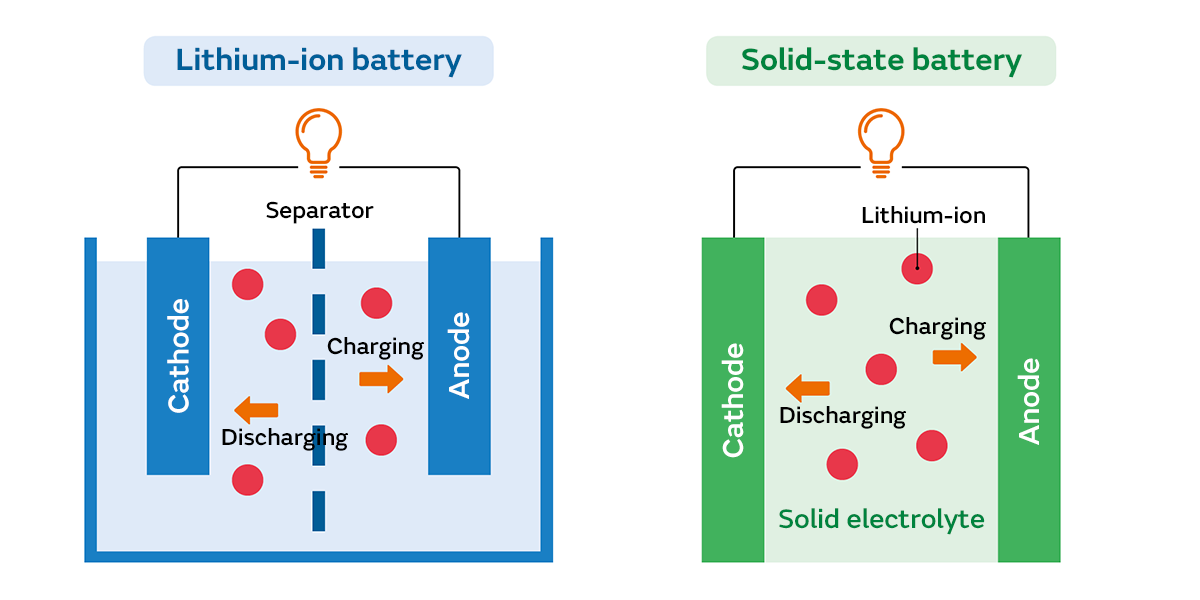
Fundamentals Of Lithium-ion Batteries
Understanding the fundamentals of Lithium-Ion batteries is crucial. These batteries power many of our daily devices. They are common in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
Key Components And Function
Lithium-ion batteries include several vital parts:
- Anode (usually graphite)
- Cathode (metal oxide)
- Electrolyte (conducts lithium ions)
- Separator (keeps anode and cathode apart)
During use, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode. This movement creates energy that powers devices.
Advantages In Current Use
Lithium-ion batteries offer several benefits:
- High energy density – More power in less space
- Longer lifespan – They last many charge cycles
- Low maintenance – No need for regular upkeep
- Quick charging – They recharge faster than other types
These features make them ideal for today’s tech needs.
Solid State Batteries Explained
Imagine a world where electric cars charge in minutes. Solid-state batteries make this dream closer to reality. They are a new breed of energy storage. They offer better safety and performance than traditional lithium-ion batteries. Let’s dive into what sets solid-state batteries apart.
Core Differences From Lithium Ion
Solid-state batteries and lithium-ion batteries have fundamental differences. The most notable is the electrolyte material. Solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte. In contrast, lithium-ion batteries use a liquid electrolyte. This difference leads to various benefits for solid-state batteries.
- Safety: Solid-state batteries are less prone to catching fire.
- Longevity: They last longer than lithium-ion batteries.
- Energy Density: They hold more power in a smaller space.
Technological Innovations
Solid-state batteries are at the forefront of battery technology. They have sparked a wave of innovations. Here are a few breakthroughs:
| Feature | Innovation |
|---|---|
| Material | Solid ceramics or glass can be used as electrolytes. |
| Form Factor | Thin and flexible designs are possible. |
| Charging Speed | Rapid charging capabilities without degradation. |

Performance Metrics Compared
Regarding the future of batteries, two types often come up: solid-state and lithium-ion batteries. To understand which might power our devices tomorrow, we need to compare their performance. Let’s dive into the specifics.
Energy Density Showdown
Energy density measures how much power a battery can store relative to its size. Solid-state batteries are the rising stars here. They promise higher energy density than lithium-ion batteries. This means more power in a smaller package. Imagine your phone lasting days, not hours, on a single charge. It’s also a game-changer for electric cars, potentially offering longer ranges without increasing battery size.
Charging Speed And Efficiency
Everyone wants batteries that charge quickly and last long. Solid-state batteries might outshine lithium-ion here as well. They are designed to handle faster charging speeds. Consider filling up your car with gas and charging it simultaneously. They also have a lower risk of overheating, making them safer and more efficient. Lithium-ion batteries are catching up, but solid-state technology could lead the race.
Safety And Durability
The quest for safer and more durable batteries is leading the charge in technology today. In the battery world, solid-state and lithium-ion are two key players. Let’s dive into how these technologies compare safety and durability.
Reducing Risks With Solid State
Solid-state batteries eliminate flammable liquid electrolytes. They have a lower chance of catching fire as a result. Solid-state batteries offer peace of mind in cars, gadgets, and homes.
- Higher resistance to temperature changes
- Less prone to thermal runaway
- Robust against physical damage
Life Cycle And Stability
Solid-state batteries boast a longer life cycle than lithium-ion ones. They handle more charge cycles before they start to degrade. This makes them more stable over time.
| Feature | Solid State Battery | Lithium Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Charge Cycles | Higher | Lower |
| Stability | More Stable | Less Stable |
With fewer replacements needed, solid-state batteries are not just safe but also eco-friendly. They reduce waste and save resources.

Credit: www.flashbattery.tech
Economic And Environmental Impact
Battery technology’s Economic and Environmental Impact is a hot topic in today’s energy discussions. We compare solid-state batteries with traditional lithium-ion batteries. We look at cost and sustainability. We ask how they affect our wallets and our world.
Cost Analysis
Solid-state batteries promise longer lifespans and better safety. But their production is more expensive. Lithium-ion batteries cost less today. This is due to mature manufacturing processes.
Experts predict solid-state battery costs will drop. This will happen as technology improves. For now, lithium-ion batteries remain the more budget-friendly option for consumers.
Sustainability And Recycling
Solid-state batteries use fewer toxic materials. This makes them more environmentally friendly than lithium-ion batteries. They are also easier to recycle. This reduces their environmental footprint.
Lithium-ion batteries can be recycled, too. But the process is complex. It requires more energy. Recycling rates for lithium-ion batteries are low. This is a challenge for our planet.
Investments in recycling technology are growing. This will improve the sustainability of both battery types. It will also reduce the impact on the earth.
| Battery Type | Recycling Process | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-State | Easier, less toxic | Lower |
| Lithium-Ion | Complex, energy-intensive | Higher |
Challenges In Solid State Adoption
The shift from lithium-ion to solid-state batteries promises a leap in energy storage technology. Yet, solid-state batteries face several hurdles before they outpace their lithium-ion counterparts. Understanding these challenges is crucial for assessing the future of battery technology.
Manufacturing Complexities
Building solid-state batteries involves intricate processes. These differ significantly from the well-established methods used for lithium-ion batteries. Crafting the solid electrolyte requires precision and control. Manufacturers must ensure that the layers within the battery are free from defects. Any imperfections can lead to poor performance or even failure.
- High-quality materials are essential.
- Cleanroom conditions are often necessary.
- Advanced technology for layering is a must.
These factors contribute to higher production costs. They also demand a skilled workforce. Together, they slow down the adoption of solid-state batteries.
Current Market Limitations
The current market for batteries is dominated by lithium-ion technology. This dominance is due to its decades of development and cost-effective production. Solid-state batteries, however, are still in the early stages. They struggle to compete on price and availability.
| Aspect | Lithium-Ion | Solid-State |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share | High | Low |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Availability | Widespread | Limited |
Investors and consumers are often hesitant to shift towards a new technology. This is especially true when the existing one continues to improve. Companies must invest heavily in research and development. They also need to scale up production for solid-state batteries to become more accessible.

Credit: www.everythingpe.com
Future Perspectives
Imagine a world where your phone charges in minutes and your car drives for days. This future is not far off, thanks to new battery technologies. Solid-state batteries (SSB) are on the horizon, poised to revolutionize how we use and store energy. They promise higher energy density, safety, and longevity than current lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries.
Potential Applications
SSBs will change many industries. Here’s how:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): SSBs can make EVs lighter and extend their range.
- Electronics: Phones and laptops will have longer battery life and faster charging.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Solar and wind energy can be stored more efficiently, making green energy more reliable.
Roadmap For Mass Production
Creating SSBs for everyone is not simple. Companies must overcome significant challenges. Here’s a roadmap:
- Develop new materials that are both effective and affordable.
- Build advanced manufacturing facilities equipped for SSB production.
- Test SSBs extensively to ensure they meet safety and performance standards.
- Start small-scale production and gradually increase to meet global demand.
Leaders in battery tech are investing heavily to make this roadmap a reality. Mass production may start within a few years, changing our tech and world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is A Solid-state Battery Better Than Lithium?
Solid-state batteries often outperform lithium-ion ones in safety and longevity. They have a higher energy density and charge faster. However, they are currently more expensive and less available.
What Is The Problem With Solid-state Batteries?
Solid-state batteries face high costs, scalability issues, and complex manufacturing processes, which hinder widespread adoption.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Solid-state Batteries?
Solid-state batteries face high manufacturing costs and limited production scalability. They also have challenges with temperature sensitivity and currently lack a fast-charging infrastructure.
How Long Will Solid-State Batteries Last?
Solid-state batteries can last up to 15 years, depending on usage and conditions. They typically offer longer lifespans and better safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Conclusion
Solid-state batteries are poised to revolutionize the energy storage landscape. They offer advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries with superior safety, longevity, and energy density. As technology advances, the choice between solid state and lithium-ion will hinge on specific needs and applications.
Embracing innovation, the battery industry is set to power a more efficient future.

I am a battery specialist writer and blogger based in the USA & UK . I have been working with battery power energy for 3 long years and I give trips on low battery power problem and solutions . I have a lot of experience with battery power and I share them here.
