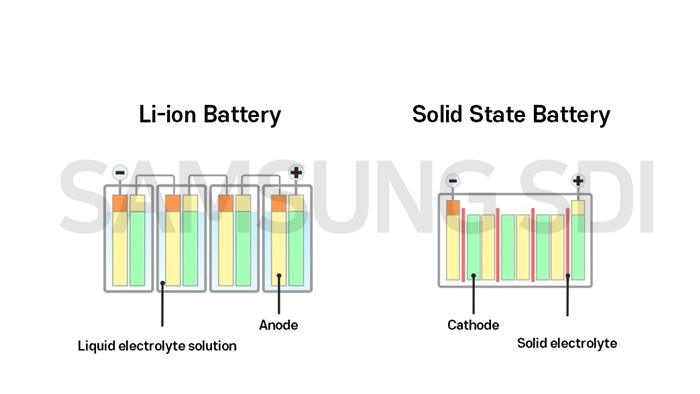
Solid-state batteries offer higher energy density and safety than traditional lithium-ion batteries. They use solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones, marking a significant technological advancement.
Exploring the future of energy storage, we find ourselves at a crossroads between traditional lithium-ion batteries and their promising successor, solid-state batteries. This innovative leap forward presents a game-changer in battery technology, promising to revolutionize everything from electric vehicles to portable electronics.
Solid-state batteries stand out for their robustness, offering increased energy density, which translates to longer-lasting power and shorter charging times. They also boast a reduced risk of fire and leakage due to their solid electrolytes. On the other hand, lithium-ion batteries have dominated the market for decades, providing reliable power with a well-established manufacturing infrastructure. The transition to solid-state technology is a matter of improved performance and overcoming production and scalability challenges. The shift to solid-state batteries could be pivotal in powering our future as the world leans towards more sustainable and efficient energy solutions.
Credit: article.murata.com
Solid-State Battery vs Lithium-Ion
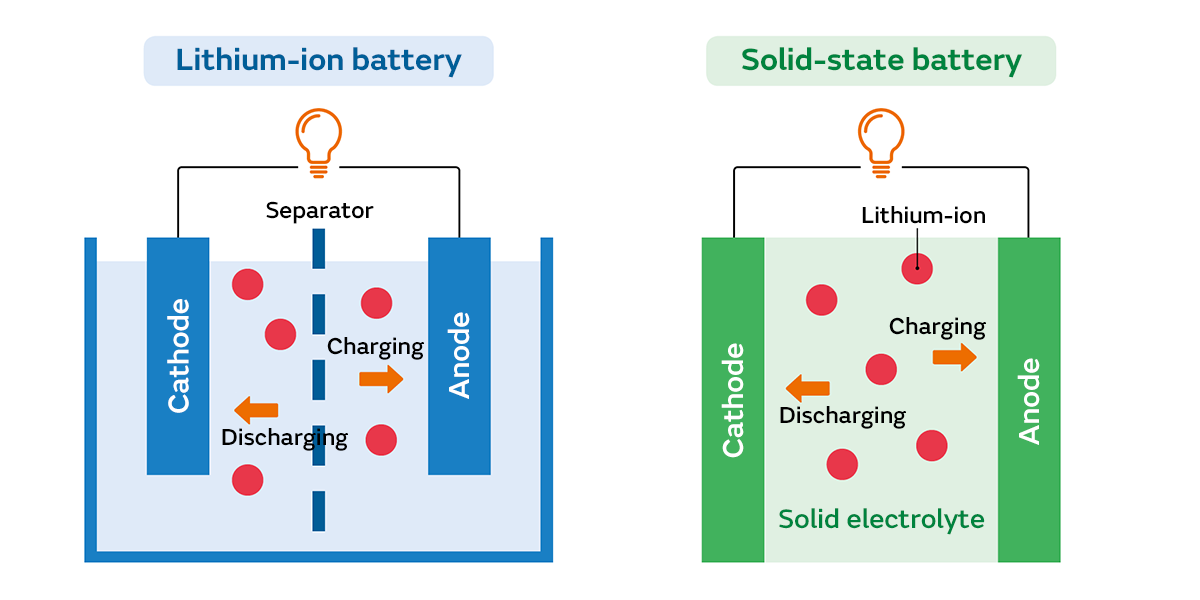
Solid-state and lithium-ion batteries represent two significant evolutions in rechargeable battery technology, each with distinct advantages. Lithium-ion batteries, ubiquitous in today’s electronic devices and electric vehicles, utilize a liquid electrolyte solution to facilitate the flow of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charge and discharge cycles.
This design has proven effective, offering high energy density and long cycle life, but it is not without drawbacks, including risks of leakage and thermal runaway leading to potential fires. On the other hand, solid-state batteries replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid electrolyte, reducing the risk of leakage and fires and potentially increasing energy density. This could lead to safer batteries, lasting longer and holding more charge, providing a fantastic range for electric vehicles. However, solid-state technology is still under development and faces challenges in manufacturing scalability and costs compared to the more mature lithium-ion technology.
Introduction To Battery Evolution
The journey of battery technology has been a tale of innovation and breakthroughs. From the early days of lead-acid batteries to the modern lithium-ion cells, each step has paved the way for more power in smaller packages.
From Lead-acid To Lithium-ion
Batteries have changed a lot since the days of lead-acid batteries. Lead-acid batteries were the first recharging batteries used in business. They were created in 1859. They powered early cars and were the backbone of energy storage for years. But they were heavy and had a low energy-to-weight ratio.
Enter lithium-ion batteries. Sony commercialized them in 1991. These batteries were a game changer. They offered higher energy density, meaning more power and longer life in a lighter package. Today, lithium-ion is the standard for portable electronics and electric vehicles.
Emerging Solid-state Technology
Now, the spotlight is on solid-state batteries. Unlike liquid or gel forms in lithium-ion batteries, they use solid electrodes and a solid electrolyte. Solid-state batteries promise even higher energy density and safety. They could charge faster and last longer.
Researchers are working hard to overcome challenges in solid-state technology. They aim to make these batteries affordable and available for everyday use.
Basics Of Lithium-ion Batteries
The Basics of Lithium-Ion Batteries form the cornerstone of modern portable energy. Widespread in electronics, these batteries power everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. With a high energy density, they offer long-lasting power in a compact form. Let’s dive into how they work and weigh their advantages against the drawbacks.
How Lithium-ion Batteries Work
Lithium-ion batteries work because lithium ions move around inside them. These ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode when discharging and back when charging. This flow generates an electric current that is used to power devices.
| Charge | Discharge |
|---|---|
| Lithium ions move to the negative electrode | Ions move to the positive electrode |
| Battery stores energy | Electric current powers devices |
Pros And Cons
- Pros:
- High energy density
- Long lifespan
- Low self-discharge rate
- Cons:
- Sensitive to high temperatures
- Degradation over time and use
- Higher cost compared to other batteries
Exploring Solid-state Batteries
The energy landscape buzzes with excitement about solid-state batteries. These powerhouses promise a leap in technology, offering a glimpse into the future of energy storage. Unlike their lithium-ion cousins, solid-state batteries employ a solid electrolyte. This shift in design could revolutionize our electronic devices, electric vehicles, and the way we store renewable energy.
What Sets Solid-state Apart
Solid-state batteries stand out from lithium-ion batteries in their core design. Lithium-ion batteries use a liquid electrolyte solution; solid-state batteries use a solid one. This difference is key to their unique benefits. The solid electrolyte is typically made from ceramic or glass, eliminating the flammable liquid found in lithium-ion batteries.
Potential Advantages
- Increased safety: With no liquid to leak or catch fire, solid-state batteries reduce the risk of accidents.
- Longer life: Solid-state batteries can endure more charge cycles, meaning they last longer.
- Faster charging: These batteries have the potential to charge much quicker than lithium-ion batteries.
- Higher energy density: More energy can be stored in a smaller space, which is great for devices and electric cars.
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Battery | Solid-State Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Type | Liquid | Solid |
| Safety | Lower | Higher |
| Lifespan | Shorter | Longer |
| Charging Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Energy Density | Lower | Higher |

Credit: www.flashbattery.tech
Comparative Analysis
In our Comparative Analysis, we explore critical differences between solid-state batteries and lithium-ion batteries. We focus on energy density, safety, stability, lifespan, and degradation.
Energy Density Comparison
Energy density measures how much power a battery can hold. Solid-state batteries often outperform lithium-ion ones in this area.
| Type of Battery | Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|
| Solid-State Battery | Approx. 500-1000 Wh/kg |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Approx. 150-260 Wh/kg |
Safety And Stability
Solid-state batteries are safer than lithium-ion. They are less likely to catch fire.
- Solid-state batteries use solid electrolytes.
- Lithium-ion batteries use liquid electrolytes.
Lifespan And Degradation
Solid-state batteries last longer than lithium-ion ones. They degrade slower.
- Solid-state can last over 10,000 cycles.
- Lithium-ion typically lasts about 1,000-3,000 cycles.
Environmental Impact
Choosing between solid-state batteries and lithium-ion technology is not just about power and performance. The environment plays a key role. We must consider the Earth’s well-being. Let’s explore how these batteries stack up in terms of environmental impact.
Recycling Challenges
Solid-state batteries promise safer recycling than traditional lithium-ion cells. They contain less toxic material. Yet, recycling infrastructure is not fully ready for them. Lithium-ion batteries have been around longer. Their recycling processes are more developed but not perfect.
- Lithium-ion batteries: Complex recycling due to mixed materials.
- Solid-state batteries: Need for new recycling methods.
Carbon Footprint Considerations
The production phase matters. It determines a battery’s initial carbon footprint. Solid-state batteries use less energy during manufacturing. This leads to lower emissions. Lithium-ion batteries are improving. However, their production still releases more carbon dioxide.
| Battery Type | Energy Use in Production | Carbon Dioxide Emissions |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion | Higher | More |
| Solid-State | Lower | Less |
Both types need transport. This adds to their carbon footprint. Solid-state batteries are lighter. They cost less to move. This means fewer emissions from transport.
Market Readiness And Adoption
The transition to more efficient and durable battery technologies is critical in today’s tech-driven world. Consumers and industries alike are eager to see how solid-state batteries’ market readiness and adoption rates compare to well-established lithium-ion batteries.
Current Market Position Of Lithium-ion
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market. From cell phones to electric cars, they power everything. Their widespread use comes from years of development, leading to a mature market with optimized production lines. Manufacturers have also invested significantly in lithium-ion technology, ensuring a solid supply chain. This has resulted in various products with reliable performance at competitive prices.
- Widespread use in consumer electronics and EVs
- An established supply chain ensures steady production
- Cost-effective solutions due to mature technology
Solid-state Batteries: Commercial Viability
Solid-state batteries promise higher energy density and improved safety over lithium-ion. But, their commercial viability is still under scrutiny. Production challenges and high costs are barriers to their entry into the market. Despite this, significant investments are flowing into research and development. Companies aim to overcome these barriers and bring solid-state batteries to the forefront of energy storage solutions.
| Aspect | Solid-State Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Higher | Lower |
| Safety | Improved | Good |
| Cost | Currently high | More affordable |
| Market Readiness | Developing | Mature |
Early adopters and specific niche markets are showing interest in solid-state technology. The automotive and aerospace industries are potential critical players in its adoption. They seek the benefits of higher energy capacity and safety that solid-state batteries could provide. The race is on to make solid-state batteries a market leader, but lithium-ion remains the go-to choice for now.
Applications In Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) need robust, reliable batteries. Solid-state batteries and lithium-ion batteries are popular choices. Each type has unique benefits for EVs.
Ev Battery Requirements
EV batteries must meet high standards to be effective. Key requirements include:
- Long life: Batteries should last many years.
- High energy density: They store a lot of energy.
- Fast charging: Charging should be quick and easy.
- Safety: Batteries must be very safe to use.
Implications For Ev Performance
The type of battery in an EV affects how it performs. Let’s look at how:
| Battery Type | Energy Density | Safety | Charging Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-State | High | Very safe | Medium |
| Lithium-Ion | Medium | Less safe | High |
Solid-state batteries are safer and have more energy. But lithium-ion batteries charge faster.

Credit: www.everythingpe.com
Looking Towards The Future
As we gaze into the energy landscape of tomorrow, the rivalry between solid-state batteries and lithium-ion technology heats up. Pioneering discoveries in the battery domain are poised to redefine our approach to power storage and device longevity. This evolution promises to touch everything from electric vehicles to portable electronics, making understanding the upcoming changes crucial.
Innovations On The Horizon
The race is on to unlock new battery potentials. Solid-state batteries stand out with their promise of higher energy densities and safety. Teams worldwide are working on materials like lithium metal, which could dramatically increase storage capacity. These batteries could also charge faster, making them ideal for a world that never slows down.
- Solid-state batteries may last longer than lithium-ion.
- They have the potential to charge in minutes, not hours.
- Solid-state technology can reduce fire risks in devices.
On the other side, lithium-ion isn’t bowing out. Innovations aim to make these batteries more robust and eco-friendly. Researchers are improving recycling methods and exploring ways to harvest lithium more sustainably.
| Feature | Solid-State Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Higher | Lower |
| Safety | Better | Good |
| Charging Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Longevity | Longer | Shorter |
Predicting The Power Shift
As we witness the dawn of solid-state dominance, we must prepare for a power shift. The signal is evident in the fact that automotive giants like Toyota and Volkswagen are investing heavily. Solid-state is not a distant dream; it’s an imminent reality. The transition could begin within this decade, with some experts pointing to 2025 for the first wave of solid-state powered electric vehicles.
The impact extends beyond cars. Imagine smartphones that need a charge just once a week or laptops that run for days. This is the future solid-state technology can unlock. While lithium-ion has laid the groundwork, solid-state is poised to leapfrog, offering a new energy paradigm.
Yet, challenges remain. Scaling up production and reducing costs are hurdles solid-state must overcome. Lithium ion won’t vanish overnight; it will evolve and power our lives. But with solid-state advancements, the shift is not ‘if’ but ‘when’. This power shift will spark a revolution, forever changing how we interact with technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is A Solid-state Battery Better Than Lithium?
Solid-state batteries typically offer higher energy density, longer lifespan, and improved safety than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
What Is The Problem With Solid-state Batteries?
Solid-state batteries face high costs, manufacturing complexities, and limited large-scale production capabilities. They also require further development to improve energy density and charging speed.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Solid-state Batteries?
Solid-state batteries have high production costs and limited availability and are currently less scalable than traditional lithium-ion batteries. They also face challenges in temperature sensitivity and long-term durability.
How Long Will Solid-State Batteries Last?
Solid-state batteries can last over 20 years with proper usage, offering up to 2. 5 times the lifespan of traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Conclusion
Choosing between solid-state batteries and lithium-ion technology depends on your specific needs. Solid-state offers enhanced safety and longevity, which is ideal for future innovations. Meanwhile, lithium-ion remains accessible and cost-effective for today’s devices. Each has its merits, making them pivotal in advancing battery technology.
Consider your priorities to make the best choice.