Lithium batteries offer higher energy density and longer lifespan than alkaline batteries. Alkaline batteries are cost-effective and readily available for daily use.
Selecting lithium and alkaline batteries depends on the intended application and performance requirements. Consumers often choose between these two popular battery types, each with distinct advantages. Lithium batteries stand out in high-drain devices and extreme temperature conditions, providing consistent power over time.
On the other hand, alkaline batteries are the go-to option for standard household devices due to their affordability and reliable performance under moderate load. This introduction sets the stage for a deeper dive into the nuanced comparison of lithium and alkaline batteries, guiding readers towards making an informed decision based on their specific needs. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each battery type is essential for optimizing device functionality and cost-effectiveness.

Lithium Battery Vs Alkaline Battery
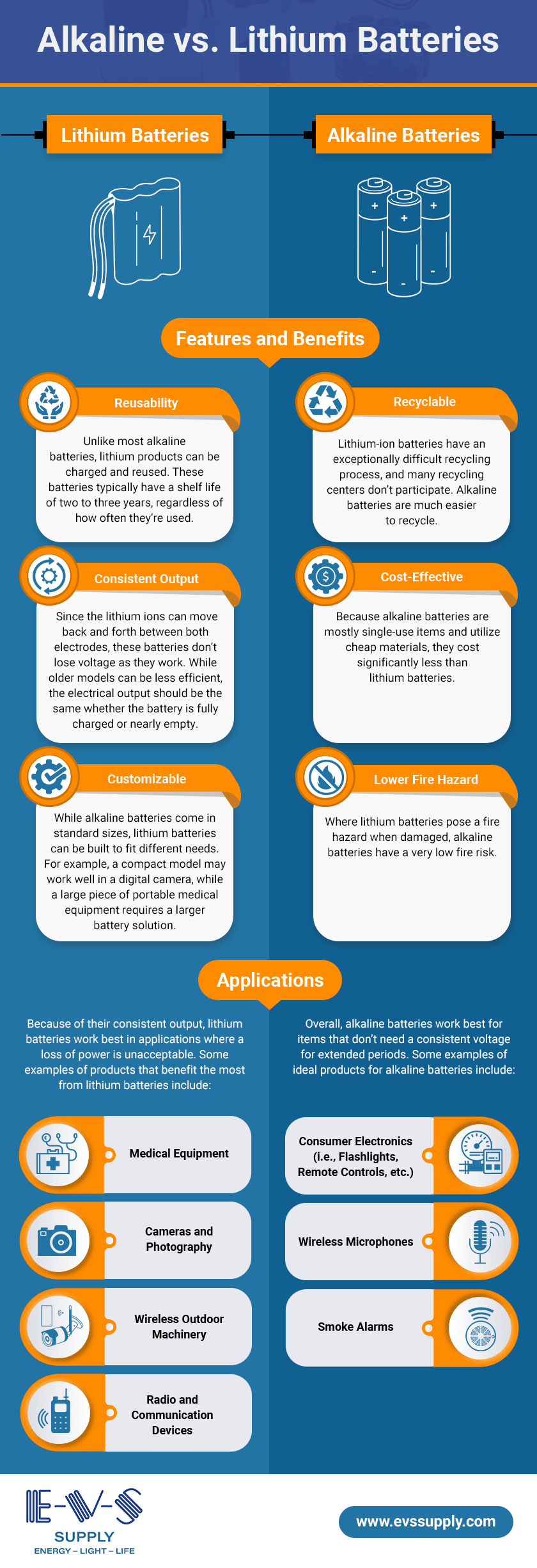
Lithium batteries and alkaline batteries serve different purposes based on their unique strengths. Lithium batteries, notable for their lightweight and high energy density, offer a superior performance, especially in devices that require a consistent and long-lasting source of power. They excel in extreme temperature conditions, making them the go-to choice for high-drain devices such as digital cameras and flashlights. Alkaline batteries, on the other hand, provide a cost-effective solution for everyday electronic needs. They’re commonly used in low-drain devices like remote controls and wall clocks due to their lower initial cost and satisfactory performance under typical conditions. While lithium batteries stand out for their efficiency and longevity, alkaline batteries remain a reliable and affordable option for less demanding applications.
Introduction To Battery Technology
Welcome to the electrifying world of battery technology. Batteries power our lives, from the remote controls in our hands to the cars we drive. They come in various shapes, sizes, and chemistries, each with unique benefits. This blog post spotlights two popular types: lithium and alkaline batteries. Let’s dive into the basics of these power sources.
Lithium Battery Basics
Lithium batteries stand out for their high energy density. This means they last longer than many other types. They are the go-to choice for devices needing long-lasting power. Cameras, smartphones, and laptops often use lithium batteries. These batteries perform well, even in extreme temperatures. Below are key points about lithium batteries:
- Lightweight: They are lighter than many other batteries, making them perfect for portable gadgets.
- Rechargeable: Many lithium batteries are rechargeable, offering extended use over time.
- High voltage: They provide more per cell, meaning fewer cells are needed for the same power output.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Long Life | They don’t need frequent replacements, saving time and money. |
| Low Self-discharge | They keep their charge for longer when not in use. |
Alkaline Battery Fundamentals
Alkaline batteries are widely used in household items. Think toys, clocks, and flashlights. They are known for their reliability and safety. Alkaline batteries have a long shelf life. This makes them a good choice for devices used less often. Here’s what sets alkaline batteries apart:
- Cost-effective: They are cheaper per unit compared to lithium batteries.
- Readily available: You can find them in nearly any store.
- Safe: They have a stable chemistry that reduces the risk of leaks or bursts.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Good Performance | They work well for everyday devices that don’t need too much power. |
| No Need to Charge | They are ready to use right out of the package, with no charging required. |

Chemical Composition And Reactions
Understanding batteries’ chemical composition and reactions can help us make informed choices. Let’s dive into the unique chemistry of lithium and alkaline batteries.
Lithium Battery Chemistry
Lithium batteries stand out for their high energy density. They harness lithium’s reactive nature.
- Between the anode and the cathode, lithium ions travel.
- The cathode often includes lithium metal oxide.
- The anode is typically made from carbon.
- Electrolytes allow ion flow without electron transfer.
Lithium ions flow from the anode to the cathode during use and then back when charging.
Alkaline Battery Chemistry
Alkaline batteries are renowned for their dependability and extended shelf life.
| Component | Material |
|---|---|
| Cathode | Manganese dioxide |
| Anode | Zinc metal |
| Electrolyte | Potassium hydroxide |
Zinc and manganese dioxide react chemically to produce energy during discharge.
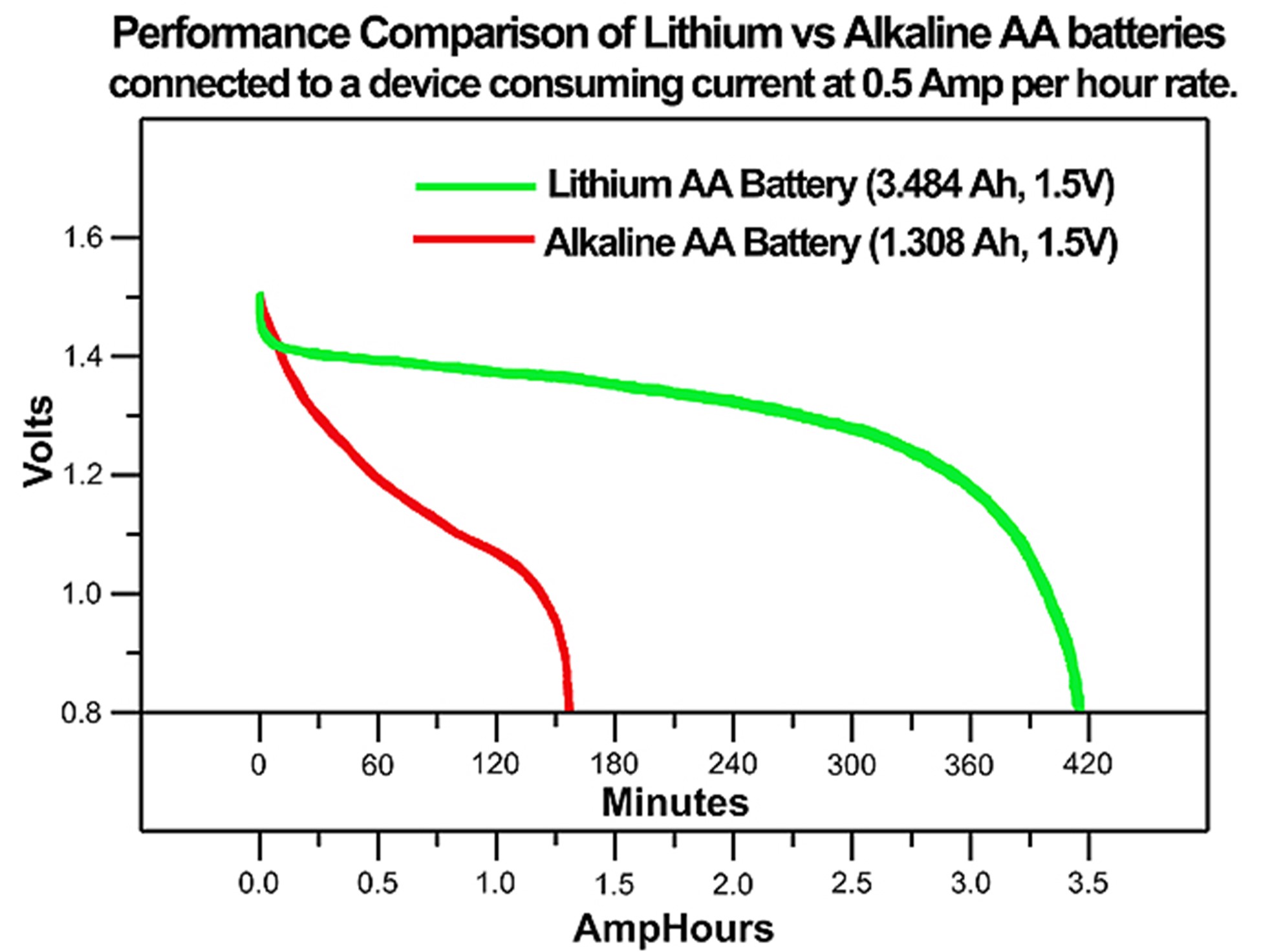
Voltage And Energy Density Comparison
Choosing the correct battery for a device involves understanding voltage and energy density. These factors determine how long a battery will last and how well it will perform. Let’s compare lithium batteries with alkaline batteries under these two crucial aspects.
Standard Voltages
Every battery type has a typical voltage at which it operates. This is important for powering devices correctly.
- Lithium batteries usually have a standard voltage of 3.0 volts.
- Alkaline batteries typically provide 1.5 volts.
This means lithium batteries can deliver more power from a single cell than alkaline batteries.
Energy Density Metrics
Energy density is a key performance indicator. It tells us how much energy a battery contains about its size or weight.
| Type of Battery | Density of Energy (Wh/kg) | The density of Energy (Wh/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium | 100-265 | 250-670 |
| Alkaline | 80-110 | 200-350 |
Lithium batteries have a higher energy density. This means they are lighter and can store more energy than alkaline batteries of the same size.
Lifespan And Longevity
Lifespan and Longevity are key factors when choosing between lithium and alkaline batteries. Each type offers distinct advantages and disadvantages that impact how long they last before needing replacement.
Shelf Life
Lithium batteries excel in shelf life. They can last up to 20 years without use. This makes them ideal for devices used in emergencies, like flashlights and smoke detectors. Alkaline batteries, in contrast, have a shorter shelf life of around 5 years. Below is a comparison:
| Battery Type | Shelf Life |
|---|---|
| Lithium | Up to 20 years |
| Alkaline | About 5 years |
Cycle Life
Lithium batteries also lead to cycle life. They handle hundreds of charge and discharge cycles. This trait suits high-use devices like cameras and gaming controllers. Alkaline batteries do not support recharging well. They are better for low-drain devices such as wall clocks and remote controls. See the details below:
- Lithium: Effective for high-drain devices
- Alkaline: Best for low-drain applications
Remember, choosing the correct battery depends on the device’s needs and expected longevity.

Environmental Impact And Disposal
The choices we make regarding batteries affect our planet. Let’s examine lithium and alkaline batteries’ environmental impact and disposal differences.
Eco-friendly Options
Lithium batteries boast a longer life and reduce waste. However, their disposal raises concerns. The toxic materials inside them can harm the environment.
Alkaline batteries are less risky and contain fewer harmful chemicals. However, they don’t last as long and create more waste over time.
Rechargeable options exist. They cut down on waste. They are a greener choice.
Recycling Protocols
Recycling batteries is critical. It keeps dangerous materials out of landfills. Both battery types have specific recycling rules.
- Lithium batteries must be taken to special facilities. They need careful handling. This prevents fires and pollution.
- Alkaline batteries are more accessible to recycle. Many places accept them. However, not all regions have programs in place.
Check local guidelines. Find proper disposal sites. Be part of the solution.
| Battery Type | Recycling Process | Drop-off Locations |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium | Handle with care | Special facilities |
| Alkaline | More common | Many places |
Credit: support.simpleaccess.com
Cost Analysis
Understanding the cost of batteries is critical to making intelligent choices. Let’s dive into lithium and alkaline batteries’ price points and long-term value.
Price Points
Initially, lithium batteries are frequently more expensive. Alkaline batteries are more budget-friendly at purchase.
| Battery Type | Average Cost |
|---|---|
| Lithium | $1.50 – $3.00 per battery |
| Alkaline | $0.50 – $1.00 per battery |
Long-term Value
Lithium batteries last longer. They offer a better return over time. Alkaline batteries may need more frequent replacement.
- Lithium: up to 10 years of shelf life
- Alkaline: 5-7 years shelf life
In devices, lithium can outlast alkaline by 4 to 6 times. This reduces waste and the need to buy new batteries.
Performance In Extreme Conditions
Discussing batteries’ Performance in Extreme Conditions is crucial. Users need reliable power sources, especially in harsh environments. Let’s explore how lithium and alkaline batteries perform under such conditions.
Temperature Tolerance
Lithium batteries excel in extreme temperatures. They operate well in both very cold and very hot climates. In contrast, alkaline batteries lose efficiency as the temperature deviates from room temperature. Below is a comparison of their performance:
| Type | Cold Temperature Performance | Hot Temperature Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium | Effective down to -40°C | Effective up to 60°C |
| Alkaline | Decreases below 0°C | Decreases above 45°C |
Durability Under Stress
Lithium batteries are more durable under physical stress than alkaline batteries. They are built to withstand impacts and vibrations that are common in extreme conditions. Here are some key points:
- Lithium: Resists sudden impacts and vibrations.
- Alkaline: May break or leak under stress.
This makes lithium batteries a safer and more reliable choice for demanding applications.

Credit: m.youtube.com
Applications And Suitability
Choosing the correct battery depends on the device and its power needs. Lithium and alkaline batteries each have unique strengths. They fit different applications. Let’s explore where they work best.
Consumer Electronics
Lithium batteries are the top choice for consumer electronics. They’re lightweight and provide long-lasting power. This makes them perfect for daily use items like:
- Smartphones
- Laptops
- Cameras
Alkaline batteries are cost-effective. They’re suitable for low-drain devices such as:
- Remote controls
- Wall clocks
- Flashlights
Industrial Uses
In the industrial sector, battery choice is crucial. Lithium batteries are favoured for their high energy density. They power:
- Medical equipment
- Security systems
- Backup power supplies
Alkaline batteries are reliable for less demanding applications. Industries use them in:
- Safety equipment
- Portable radios
- Industrial clocks
Safety Concerns
Battery safety Concerns are vital to consider. Lithium and alkaline batteries power our devices differently, and each has unique risks. Users must understand these risks to stay safe. This section dives into the safety issues of these battery types.
Leakage Risks
Lithium and alkaline batteries can leak under certain conditions. Leaks can damage devices and harm skin and eyes. Let’s compare their leakage risks.
- Lithium batteries: Rarely leak. They can still release hazardous chemicals if damaged.
- Alkaline batteries are more prone to leakage. The leak is often a corrosive liquid that can cause chemical burns.
Fire Hazards
Fire risks are a serious concern with any battery. Overheating, short-circuiting, or improper use can lead to fires. Here’s how lithium and alkaline batteries stack up.
| Battery Type | Fire Risk |
|---|---|
| Lithium | High energy density. It can catch fire if punctured or charged improperly. |
| Alkaline | Lower energy density. Less likely to catch fire but still possible with misuse. |

Innovation And Future Prospects
The world of batteries is buzzing with innovation. As we look towards the future, two leading players emerge: lithium and alkaline batteries. Each has its own set of advantages and is evolving rapidly to meet the demands of modern technology. Let’s delve into the innovations and prospects shaping the energy landscape.
Technological Advancements
Lithium batteries have taken the lead in innovation. They are lighter and offer a higher energy density. This means they can last longer than alkaline batteries. Lithium batteries are also rechargeable. This makes them a favourite for electronics like smartphones and laptops.
Alkaline batteries are also improving. They are now more reliable and have a longer shelf life, making them perfect for devices like remote controls and clocks.
- Smart technology integration allows batteries to communicate with devices.
- Advances in nanotechnology are making batteries more diminutive and more powerful.
- Improved cathode materials boost performance and safety.
Emerging Alternatives
Research is pushing boundaries beyond lithium and alkaline options. Scientists are exploring new materials. They aim to make batteries greener and more efficient. Below are some promising alternatives:
| Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Solid-State Batteries | Higher energy density and safety |
| Graphene Batteries | Fast charging and longevity |
| Bio-Batteries | Eco-friendly and renewable |
These emerging alternatives could redefine how we store and use energy. They are the key to a more efficient and sustainable future. Keep an eye on these developments as they accelerate towards reality.
Credit: www.evssupply.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Batteries Are Better, Alkaline Or Lithium?
Lithium batteries offer longer life and better performance in extreme temperatures than alkaline batteries.
What Happens If I Replace My Lithium Batteries With Alkaline Batteries?
Using alkaline batteries instead of lithium can result in lower performance and shorter lifespan, as they have different voltage and discharge rates. Always check device compatibility.
What Would Happen If You Put Alkaline Batteries in the Blink Instead of Lithium?
Using alkaline batteries in Blink cameras instead of lithium may result in reduced performance and shorter battery life.
Are Duracell Batteries Alkaline Or Lithium?
Duracell offers both alkaline and lithium batteries. Their alkaline batteries are commonly used for everyday devices, while lithium batteries are designed for high-drain or long-lasting needs.
Conclusion
Choosing between lithium and alkaline batteries depends on your needs. Lithium batteries excel in longevity and performance, especially in high-drain devices. Alkaline batteries, meanwhile, are cost-effective for regular use. Each type has its benefits, making them suitable for different applications.
Consider your device’s requirements and usage patterns before deciding.

